Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a material removal or manufacturing technique. It was first introduced in 1770 by Joseph Priestly. However, with the modernization of technology and equipment, this technology is now integrated with computer numerical control (CNC). The EDM process involves the use of thermal energy to remove excess material from an object to create the desired shape for the task.
It is not the most popular CNC machining process. However, engineers rely on it to make parts that cannot be processed. It does not require or use mechanical force to remove excess material. This is why many people think it is an unconventional manufacturing process. This process facilitates shaping and processing for a wide range of industries. In this article, we will study its working principle, the various types available, and its advantages and applications.

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Overview
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a process of removing material by exposing it to repetitive controlled electrical discharges. It is suitable for thermoelectric phenomena. When a discharge occurs between the electrode/wire and the workpiece, heat energy is generated on the workpiece. This leads to the removal of the material layer. Generally speaking, EDM is divided into three types: Die-sink EDM, small fast hole EDM and wire-cut EDM. However, in modern production processes, wire EDM machine tools are integrated with CNC. Therefore, automated EDM machines are commonly used in the industry.
This is a highly accurate process and does not involve the use of tools on the workpiece. When you need to process hard materials or form complex shapes, EDM is usually your best choice.
How Does Electrical Discharge Machining Work?
Although the definition may seem simple, the physical process is more complicated. The use of EDM to remove material from the workpiece is achieved by a series of repeated rapid current discharges between the electrodes. These electrodes are separated using dielectric fluid. Then, the voltage is sent through the dielectric fluid. It should be noted that EDM manufacturing is only suitable for conductive materials.
One of these electrodes is used to change the shape to suit the exact purpose. The electrode is a workpiece electrode or “anode”. The most commonly used electrode materials are copper, tungsten alloy, cast iron, steel, silver tungsten alloy, and graphite. The other electrode is the tool electrode or “cathode”. The basic principle behind this process is to corrode materials with controlled electric sparks. For this reason, the two electrodes must not touch.
A potential difference is applied between the workpiece and the electrode in the form of pulses. As the electrodes approach the workpiece, the electric field existing in the small gap between them increases. This continues until it reaches the breakdown level.
The discharge causes extreme heating of the material. Heating causes some parts of the material to melt. The stable flow of the dielectric fluid helps to remove excess material. The liquid also helps to cool down during processing.
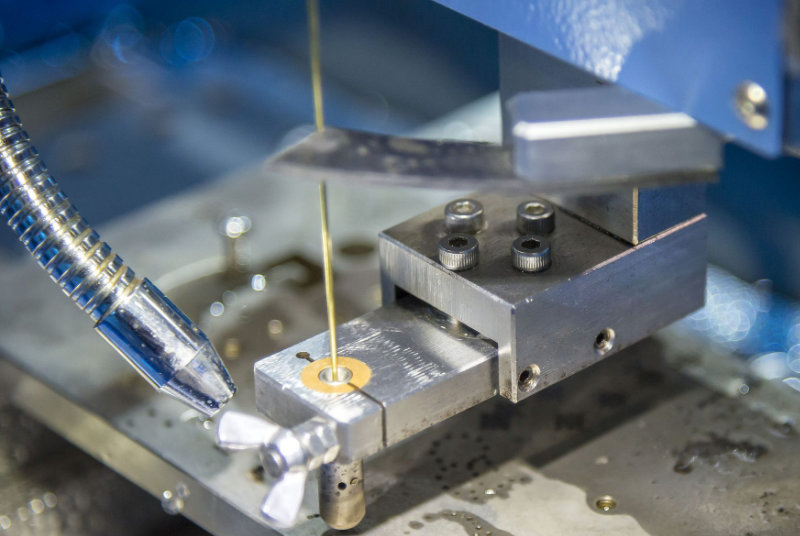
Types Of Electrical Discharge Machining
The EDM process is unique and traditional. However, this does not mean that there is only one method for this process. There are three different types of EDM. This helps to ensure that there are alternatives when a type is not suitable. Different types of electrical discharge machining include:
Wire EDM
Sometimes called wire erosion or spark EDM, wire EDM is a popular process. It involves using brass wire or thin copper to cut the workpiece. Here, the thin wires act as electrodes. In this case, the dielectric liquid is usually deionized water. During WEDM processing, a spool is used to continuously unwind the wire from the automatic feeding device.
This is because the discharge may be affected by the workpiece and the wire. Therefore, a new discharge path is required in the cut. This method is very effective. However, the engineer must take care that the wire must pass completely through the workpiece. Therefore, it essentially creates a 2D cut in a 3D part. You will often get results similar to traditional CNC machining processes.
Hole EDM
The hole EDM process is another type of EDM. As the name suggests, it helps to drill holes quickly. The electrode used for hole electric discharge machining is tubular, so that the dielectric fluid can easily flow through the electrode.
Unlike traditional drilling methods, hole EDM can process very small deep holes. In addition, these holes do not require any deburring. Regardless of the hardness or type of metal, this process can effectively drill precision holes faster than traditional methods.
Sinker EDM
This is the traditional EDM, also known as Ram EDM, sinking die or cavity EDM. Cavity type, because it can create complex cavity shapes for various casting applications (such as injection molding).
The process uses pre-processed copper or graphite electrodes to form the “positive” shape of the desired shape. Then, the electrode is pressed into the workpiece to create a negative film in the shape of the original material. Certain factors may affect the selection of electrode materials in EDM. These include the corrosion resistance and conductivity of the electrode, and graphite is generally easier to process than copper. However, copper is stronger and more advantageous.
Advantages Of EDM Machining:
Complex shapes that are difficult to produce with traditional cutting tools.
Extremely hard material with very tight tolerances.
For very small workpieces, traditional cutting tools may damage the parts due to excessive cutting tool pressure.
There is no direct contact between the tool and the workpiece. Therefore, fine parts and weak materials can be processed without deformation.
A good surface finish can be obtained.
Very fine holes can be drilled.
Disadvantages Of EDM Machining:
Material removal speed is slow.
Potential fire hazards associated with the use of fuel oil-based dielectrics.
Extra time and cost for creating electrodes for stamping/electric hammer EDM.
The power consumption is very high.
High power consumption.
Non-conductive materials can only be processed through specific process settings.
Application of EDM Machining
EDM is especially well-known in small batch production. Various processes can be performed using electrical discharge machining. These processes include milling, turning, and small hole drilling. This unique process is also valuable for a wide range of industries from the automotive to the aerospace industry.
EDM is able to create unique and precise shapes, helping the following applications:
Injection molding
Small hole drilling
Die casting



This post about EDM was incredibly informative! I especially appreciated the detailed explanation of the principles and working mechanism. The pros and cons section gave a balanced view, which is essential for anyone considering this technology for their projects. Looking forward to more posts like this!