In recent years, with the development of CNC machining, CNC machine tool parts have also continued to develop. CNC machining has become a necessity in many disciplines, and these disciplines need to manufacture special parts for their projects. CNC materials have been expanded to meet the needs of consumers, engineers, contractors and other fields to create solutions for very specific applications. The key to having the best finished product is to choose the right material.
There are a variety of materials to choose from, and the materials can be used for various parts with completely different purposes. Due to the wide variety of materials, choosing the right material for your application can be a challenge. By narrowing down the type of processing material most suitable for the part, the most suitable and cost-effective material can be selected. When selecting materials, the following points need to be considered.
Material Selection Consider Factors
How are the parts used?
Since CNC machining has been developed for many years, so have CNC machine tool components. Similar types of materials can be used in multiple products and lead to various functions. Are the parts used in medical equipment, automobiles, aerospace, machinery or industrial manufacturing?
Taking insulation as an example, the material used to insulate the breath analyzer may be different from the material used to provide insulation in the camera. They all serve the same purpose, but they cannot be used in the same way or the same result type. If you use the parts outdoors or in a humid environment, please use stainless steel instead of carbon steel to prevent the parts from rusting.
Stress Load
High stress loads can cause some materials to deform or even crack. When choosing the material of the part, make sure to take the stress load into consideration. Parts subject to high stress need to be processed with components that resist stress load and prevent deformation. If your part will be subjected to high stress, the material made from it will require the necessary elements to resist the load and prevent deformation.
Dimensional Tolerance
Never underestimate the importance of dimensional tolerances. It not only plays a role in material selection; it will also affect parts and assemblies, cutting methods, and the use of tools and machines. The dimensional tolerance will affect the effect of the whole process and the bottom line.
You need to know the required tolerances of the part. If you are using an old part design or sketch and you want to follow the past methods, it is best to check again if the tolerances are appropriate. Typos can easily appear in the document. Even if the information is correct, if adjustments can be made to relax the tolerances and still allow the part to perform its best, you can save money by re-evaluating the tolerances. Tight tolerances are usually more expensive.
The standard dimensional tolerances are used by default, but if you do not specify the tolerance or find that the number is incorrect, you will eventually order inappropriate parts. It takes more time to resize and/or reorder it, and in the long run, this simple initial step can help you save money.
If you are not sure of the exact tolerances of the parts you need, please do not make educated guesses, but let a professional CNC machining company help you solve it.
Operating Temperature
When selecting a material, the melting point of the material must be lower than the working temperature of the process. In addition, it must be considered whether there are fluctuations in the operating temperature, and the material needs to withstand the temperature without warping, deformation or breakdown over time.
Although some more durable materials are manufactured to withstand these changes, many materials will show signs of warping, swelling, and/or cracking over time. Extreme temperatures can also negatively affect the durability of certain materials.
When you are CNC machining materials, it is also important to understand this information, so you can ensure that the temperature generated by the cutting and forming of the part will not deform it. Establishing a connection between the operating temperature and the materials used is critical to successful design and production.
Weight and Stress Capacity
The weight of the processed material depends on how the part is used.
Heavy materials can absorb a lot of pressure. For projects that require excessive load-bearing capacity and high stress loads, heavy materials should be considered. But not suitable for weight-sensitive items.
Lightweight materials are popular in weight-sensitive projects. They are durable, use and can absorb a lot of stress, but they are more expensive. Lightweight materials are ideal for many products, but if cost is an important factor, then they may not be the best choice.
Choosing between heavy and light materials is just an example of which features are the most important for CNC machining parts. In this way, you can specify the elements that are critical to your part to make it work properly, exclude materials that do not meet these standards, and then compare costs.
Overall Cost and Material Manufacturability
The most expensive materials are usually high-strength, lightweight materials. When choosing processing materials, many factors will help make the decision. To find the most compatible material, prioritize the characteristics that are most important to the finished part. Choose materials that meet the strength curve, temperature limits and assembly requirements. Eliminate materials that do not meet these requirements, compare material costs, and then choose.
Generally, the more materials used in the part, the higher the cost. Similarly, special materials and extremely strong materials (such as titanium) will also cost more.
Looking for a company that offers a free quote and no minimum order quantity will help you reduce costs. Once all the scopes are reduced, more cost-effective materials can be used to meet most of your needs.
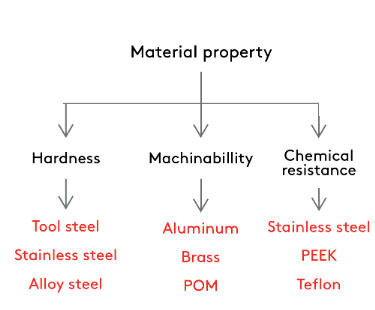
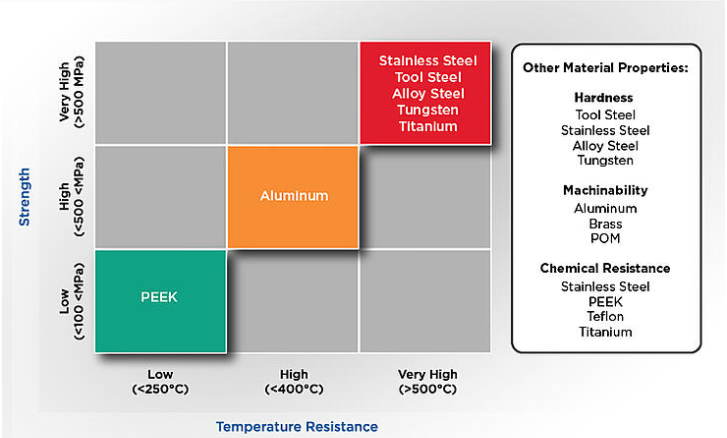
Material Selection Guidelines
SANS can process hundreds of metal, alloy and plastic materials, as well as other customized materials on request. So below we will discuss the most popular materials and their properties.
Metal
One of the most common material types in CNC milling is metal, and there is also a wide range of options. Let us get an overview of the most well-known options and the most suitable applications for each metal. Depending on the size and geometry of the part, the material cost may account for a large part of the total price of the part.
Aluminum
Aluminum is probably the most widely used material for CNC milling and is an excellent choice for mechanical parts and exterior parts. Compared with other metals, aluminum can generally be processed faster than other metals, making it the most economical method. Parts made of aluminum form a protective layer when exposed to the environment, resulting in additional strength and corrosion resistance. In view of these high-quality material characteristics, CNC milled aluminum is very suitable for use in the automotive, aerospace, healthcare and consumer electronics industries. Specific applications include aircraft accessories, electronic enclosures, medical equipment, gears and shafts.
 Aluminum 6061
Aluminum 6061
It is the most commonly used general-purpose aluminum alloy with good strength-to-weight ratio and excellent machinability. This is the most common general-purpose aluminum grade, usually used for auto parts, bicycle frames, sporting goods, RC frames, etc.
The main alloying elements are magnesium, silicon and iron. Similar to other aluminum alloys, it has a good strength-to-weight ratio and is naturally resistant to atmospheric corrosion. One of the disadvantages of 6061 is its poor corrosion resistance when exposed to salt water or other chemicals. In more demanding applications, it is not as strong as other aluminum alloys.
The composition and material properties of aluminum 6082 are similar to 6061. In Europe, it is more commonly used because it complies with British standards.
Aluminum 7075
7075 is a high-end product of aluminum. It is mainly alloyed with zinc. It is one of the strongest aluminum alloys. It is an ideal choice for high-strength entertainment equipment and automotive and aerospace frames. Because for steel, aluminum 7075 has excellent fatigue properties and can be heat treated to achieve high strength and high hardness, so it is essential to reduce weight. However, it should be avoided when welding is required.
Aluminum 5083
Aluminum 5083 has higher strength and excellent seawater resistance than most other aluminum alloys, so it is commonly used in construction and marine applications. This is also an excellent choice for welding.
More knowledge about Aluminum Parts at All about CNC Alumunium Machining
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel alloys have high strength, high ductility, excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and are easy to weld, machine and polish. Depending on their composition, they can be (essentially) non-magnetic or magnetic.
There are many types of stainless steel. It is called stainless steel because it contains chromium that helps prevent oxidation (rust). Because all stainless steel looks the same, it is necessary to use modern measurement equipment (such as OES detector) to test the incoming raw materials with extreme care to confirm the characteristics of the steel used.
Stainless Steel 303
In the case of 303, sulfur is also added. This sulfur helps make 303 the easiest stainless steel to process, but it also tends to reduce its corrosion resistance to a certain extent.
303 is not a good choice for cold forming (bending), nor can it be heat treated. The presence of sulfur also means that it is not ideal for welding. It does have excellent machining performance, but you must pay attention to the speed/feed and the sharpness of the cutting tool.
303 is usually used for stainless steel nuts and bolts, fittings, shafts and gears. However, it should not be used for marine-grade accessories.
Stainless Steel 304
It is the most common stainless steel alloy with excellent mechanical properties and good machinability. It can resist most environmental conditions and corrosive media.
This is the most common form of stainless steel found in various consumer and industrial products. Usually called 18/8, it refers to the addition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel to the alloy, which is the most common form of stainless steel.
304 is very hard, non-magnetic, easy to machine and usually has corrosion resistance, so it is very suitable for kitchen accessories, storage tanks and pipes used in industry, construction and automobile industries.
304 is easy to process, but unlike 303, it can be welded. It is also more resistant to corrosion in most normal (non-chemical) environments. For machinists, use very sharp cutting tools for processing and do not be contaminated by other metals.
Stainless Steel 316
It is another common stainless steel alloy with mechanical properties similar to 304. Usually considered to be marine grade stainless steel, tough and easy to weld. The material is very resistant to corrosion, and for salt solutions (such as sea water), it is very suitable for construction, ship fittings, industrial piping and automotive applications.
Stainless Steel 2205
Stainless steel 2205 duplex stainless steel is the strongest stainless steel alloy (twice that of other ordinary stainless steel alloys) and has excellent corrosion resistance. It is used in harsh environments and has many applications in the oil and gas industry.
17-4 Stainless Steel
The mechanical properties of 17-4 stainless steel (SAE 630 grade) are comparable to those of 304. It can be precipitation hardened to a high degree (compared to tool steel) and has excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for very high performance applications, such as the manufacture of turbine blades.
Tool Steels
Tool steels are metal alloys with exceptionally high hardness, stiffness, abrasion and thermal resistance. They are used to create manufacturing tools (hence the name), such as dies, stamps, and molds. To achieve their good mechanical properties, they must undergo a heat treatment.
 Tool steel D2 is a wear-resistant alloy that retains its hardness to a temperature of 425°C. D2 steel is an air-hardened, high-carbon, high-chromium tool steel with high wear resistance. It can be heat treated and has a strong hardness range. D2 Steel is an ideal choice for making parts and products that need to be bent easily but need to be bent.
Tool steel D2 is a wear-resistant alloy that retains its hardness to a temperature of 425°C. D2 steel is an air-hardened, high-carbon, high-chromium tool steel with high wear resistance. It can be heat treated and has a strong hardness range. D2 Steel is an ideal choice for making parts and products that need to be bent easily but need to be bent.
Tool steel A2 is an air-hardened general purpose tool steel with good toughness and excellent dimensional stability at elevated temperatures. It is commonly used to manufacture injection molding dies.
Tool steel O1 is an oil-hardened alloy with a high hardness of 65 HRC. Commonly used for knives and cutting tools.
Mild Steels
Also known as low-carbon steels and have good mechanical properties, great machinability, and good weldability. Due to their low cost, they find general-purpose applications, including the manufacturing of machine parts, jigs, and fixtures. Mild steels are susceptible to corrosion and attacks from chemicals. Commonly used are
Mild Steel 1018
Mild steel 1018 is a general-purpose alloy with good machinability and weldability, as well as excellent toughness, strength and hardness. It is the most commonly used low carbon steel alloy.
Carbon Steel 1045
This tough material is low carbon steel, Not stainless, which is usually cheaper than stainless steel, but has higher strength. The material can be hardened and heat treated to make it easy to machine and weld. It is most commonly used in industrial applications and mechanical parts that require high toughness and strength, such as nuts and bolts, gears, shafts, and connecting rods. It is also used in construction, but if exposed to the environment, it usually undergoes surface treatment to Prevent rust.
Mild steel A36
Low carbon steel A36 is a common structural steel with good weldability. It is suitable for various industrial and construction applications
Magnesium AZ31

An alloy of aluminum and zinc, magnesium AZ31 has a weight reduction of 35% compared with aluminum, but its strength is higher. However, this material is generally more expensive and is often used for aircraft components. The material is easy to process, but has flammable characteristics.
Magnesium is easy to process, but very easy to burn, especially in powder form, so it must be processed with liquid lubricants. Magnesium can be anodized to improve its corrosion resistance. It is also a highly stable structural material and an excellent choice for die castings.
Because of its light weight and high strength, it is also often used for laptop shells, power tools, camera bodies and other uses around houses.
titanium
Titanium is known for its high strength, light weight, toughness and corrosion resistance. It can be welded, passivated and anodized to enhance protection and improve appearance. Titanium has poor polishing effect and is a poor electrical conductor, but a good thermal conductor. This is a material that is difficult to process, and only professional tools can be used.
This material is usually more expensive than other metals. It is abundant in the earth’s crust, but it is difficult to refine. It is most commonly used in military, aerospace, industrial and biomedical applications.
Brass
 Recognized as one of the simplest and most cost-effective materials in CNC milling, Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, which is stable but not strong enough. Common uses include medical equipment, consumer products, and electrical hardware and contacts. Because brass also has a low coefficient of friction and high corrosion resistance, they are also used in engineering, plumbing, steam engineering, and even musical instruments. Because of its soft material and easy processing characteristics, it is used in plumbing accessories, home decoration and musical instruments.
Recognized as one of the simplest and most cost-effective materials in CNC milling, Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, which is stable but not strong enough. Common uses include medical equipment, consumer products, and electrical hardware and contacts. Because brass also has a low coefficient of friction and high corrosion resistance, they are also used in engineering, plumbing, steam engineering, and even musical instruments. Because of its soft material and easy processing characteristics, it is used in plumbing accessories, home decoration and musical instruments.
With good machinability and excellent conductivity, it is very suitable for applications requiring low friction. It is also commonly used in construction to produce a golden appearance with an aesthetic appearance.
Brass C36000 is a material with high tensile strength and natural corrosion resistance. It is one of the easiest materials to process, so it is usually used for high-volume applications.
Copper
When it comes to CNC milling materials, few metals offer the electric conductivity of copper. High corrosion resistance helps this material fight off rust, while thermal conductivity properties make the shaping process easier during CNC machining. Oftentimes utilized in the automotive industry, applications include cooling systems and heat exchangers, as well as various engineering applications like valves and radiators. However, it’s important to know that copper is weak against certain chemicals, such as acids, halogens sulphides, and ammonia solutions.
Plastics
In addition to metal materials, SANS high precision CNC machining services are also compatible with several plastics. Below are some of the most widely used plastics for CNC milling technology.
ABS
ABS is one of the most common thermoplastic materials, with good mechanical properties, excellent impact strength, high heat resistance and good machinability.
ABS has a low density, so it is very suitable for lightweight applications. CNC machined ABS parts are usually used as prototypes before mass production via injection molding.
Nylon
Nylon, also known as polyamide (PA), is a kind of thermoplastic. Due to its excellent mechanical properties, good impact strength, high chemical resistance and abrasion resistance, and also has moderate flame resistance, it is commonly used It includes insulators, bearings, and short-term products that will be used for injection molding. The disadvantage is that it easily absorbs water and moisture.
POM
POM is also called Delrin. It is an engineering thermoplastic and has the highest processability among plastics.
POM (Delrin) is usually the best choice for CNC machining of plastic parts that require high precision, high stiffness, low friction, excellent dimensional stability at high temperatures, and extremely low water absorption.
PTFE
PTFE, commonly known as polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon), is an engineering thermoplastic with excellent chemical and heat resistance and the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid. It is an excellent electrical insulator. However, it has pure mechanical properties and is often used as a lining or insert in components.
HDPE
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic with high strength-to-weight ratio, high impact strength and good weather resistance.
HDPE is a lightweight thermoplastic, suitable for outdoor use and pipeline transportation. Like ABS, it is often used to create prototypes before injection molding.
PEEK
PEEK is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability over a wide temperature range, and excellent resistance to most chemicals.
PEEK is often used to replace metal parts due to its high weight-to-weight ratio. Medical grades are also available, making PEEK also suitable for biomedical applications.




 Aluminum 6061
Aluminum 6061